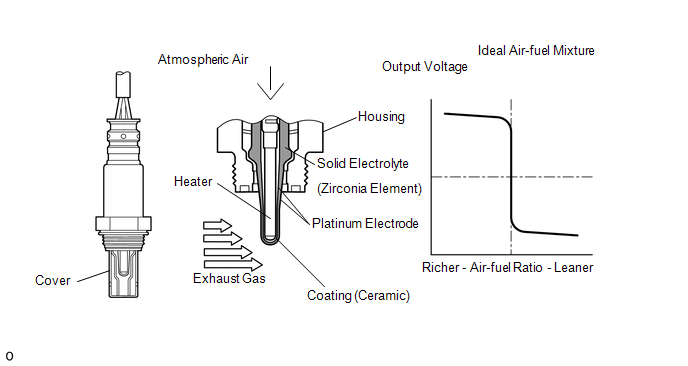
DESCRIPTION In order to
obtain a high purification rate of the carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbon
(HC) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) components in the exhaust gas, a TWC is
used. For the most efficient use of the TWC, the air-fuel ratio must be
precisely controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric
air-fuel ratio. For the purpose of helping the ECM to deliver accurate
air-fuel ratio control, a Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor is used. The
HO2 sensor is located behind the TWC, and detects the oxygen
concentration in the exhaust gas. Since the sensor is integrated with
the heater that heats the sensing portion, it is possible to detect the
oxygen concentration even when the intake air volume is low (the exhaust
gas temperature is low). When the air-fuel
ratio becomes lean, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas is rich.
The HO2 sensor informs the ECM that the post-TWC air-fuel ratio is lean
(low voltage, i.e. less than 0.45 V). Conversely,
when the air-fuel ratio is richer than the stoichiometric air-fuel
ratio, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas becomes lean. The HO2
sensor informs the ECM that the post-TWC air-fuel ratio is rich (high
voltage, i.e. more than 0.45 V). The HO2 sensor has the property of
changing its output voltage drastically when the air-fuel ratio is close
to the stoichiometric level. The ECM uses the
supplementary information from the HO2 sensor to determine whether the
air-fuel ratio after the TWC is rich or lean, and adjusts the fuel
injection time accordingly. Thus, if the HO2 sensor is working
improperly due to internal malfunctions, the ECM is unable to compensate
for deviations in the primary air-fuel ratio control.
 |
DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition |
Trouble Area | | P0136
P0156 | Either condition is met:
- Low impedance:
- Sensor impedance less than 5 Ω for more than 30 seconds when ECM
presumes sensor to be warmed up and operating normally (2 trip detection
logic)
|
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2) circuit
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2)
- Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor (for Bank 1, 2)
- Integration relay
- Gas leak from exhaust system
- EGR valve assembly
| | P0137
P0157 | Either condition is met:
- High impedance:
- Sensor impedance 15 kΩ or more for more than 90 seconds when ECM
presumes sensor to be warmed up and operating normally (2 trip detection
logic)
|
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2) circuit
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2)
- Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor (for Bank 1, 2)
- Integration relay
- Gas leak from exhaust system
- EGR valve assembly
| | P0138
P0158 |
- Extremely high voltage (short):
- HO2 sensor voltage output exceeds 1.2 V for more than 10 seconds (2 trip detection logic)
|
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2) circuit
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2)
- ECM
| | P0139
P0159 | Heated oxygen sensor voltage does not drop below 0.2 V immediately after fuel cut starts (2 trip detection logic). |
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2 Sensor 2) circuit
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2 Sensor 2)
- Gas leak from exhaust system
- EGR valve assembly
- ECM
| | P013A
P013C | Heated oxygen sensor voltage does not drop from 0.35 V to 0.2 V immediately after fuel cut starts (1 trip detection logic). |
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2 Sensor 2) circuit
- HO2 sensor (for Bank 1, 2 Sensor 2)
- Gas leak from exhaust system
- EGR valve assembly
- ECM
| MONITOR DESCRIPTION
1. Active Air-Fuel Ratio Control The
ECM usually performs air-fuel ratio feedback control so that the
Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor output indicates a near stoichiometric
air-fuel level. This vehicle includes active air-fuel ratio control in
addition to regular air-fuel ratio control. The ECM performs active
air-fuel ratio control to detect any deterioration in the Three-Way
Catalytic Converter (TWC) and Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor malfunctions
(refer to the diagram below). Active air-fuel
ratio control is performed for approximately 15 to 20 seconds while
driving with a warm engine. During active air-fuel ratio control, the
air-fuel ratio is forcibly regulated to become lean or rich by the ECM.
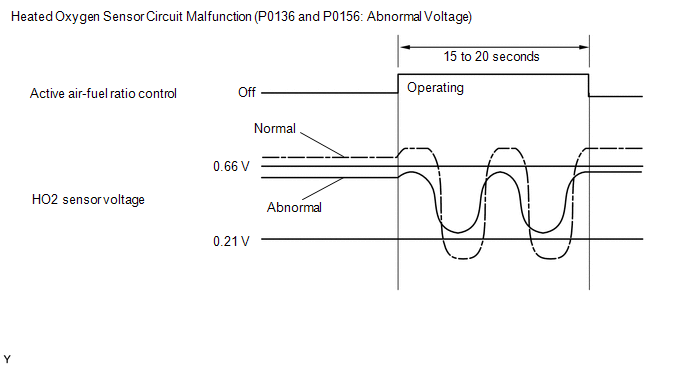
If the ECM detects a malfunction, a DTC is stored. 2. Abnormal Voltage Output of Heated Oxygen (HO2) Sensor (DTC P0136 and P0156)
While
the ECM is performing active air-fuel ratio control, the air-fuel ratio
is forcibly regulated to become rich or lean. If the sensor is not
functioning properly, the voltage output variation is small. For
example, when the HO2 sensor voltage does not increase to more than 0.66
V during active air-fuel ratio control, the ECM determines that the
sensor voltage output is abnormal and stores DTC P0136 or P0156.
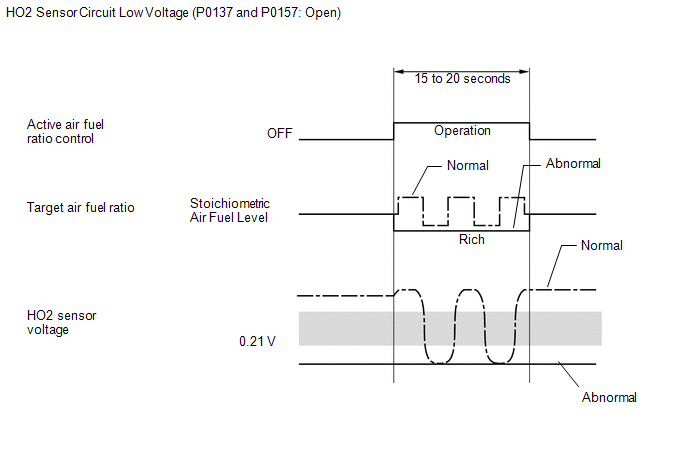
 3. Open in Heated Oxygen (HO2) Sensor Circuit (DTC P0137 and P0157)
During
active air-fuel ratio control, the ECM calculates the Oxygen Storage
Capacity (OSC)* of the Three-Way Catalytic Converter (TWC) by forcibly
regulating the air-fuel ratio to become rich or lean. If
the HO2 sensor has an open, or the voltage output of the sensor
noticeably decreases, the OSC indicates an extraordinarily high value.
Even if the ECM attempts to continue regulating the air-fuel ratio to
become rich or lean, the HO2 sensor output does not change. While
performing active air-fuel ratio control, when the target air-fuel
ratio is rich and the HO2 sensor voltage output is 0.21 V or less
(lean), the ECM interprets this as an abnormally low sensor output
voltage and stores DTC P0137 or P0157. HINT: *:
The TWC has the capability to store oxygen. The OSC and the emission
purification capacity of the TWC are mutually related. The ECM
determines whether the catalyst has deteriorated, based on the
calculated OSC value (See page  ). ).
 4. High or Low Impedance of Heated Oxygen (HO2) Sensor (DTC P0136 and P0156 or P0137 and P0157)
During
normal air-fuel ratio feedback control, there are small variations in
the exhaust gas oxygen concentration. In order to continuously monitor
the slight variation of the HO2 sensor signal while the engine is
running, the impedance* of the sensor is measured by the ECM. The ECM
determines that there is a malfunction in the sensor when the measured
impedance deviates from the standard range.
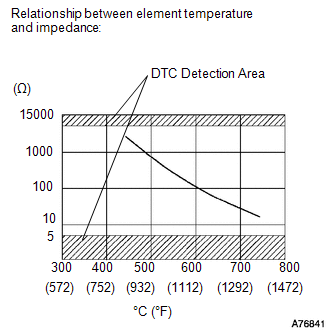 *: The effective resistance in an alternating current electrical circuit.
HINT:
- The impedance cannot be measured using an ohmmeter.
- DTCs P0136 and P0156 indicate the deterioration of the HO2 sensor. The
ECM stores the DTCs by calculating the impedance of the sensor when the
typical enabling conditions are satisfied (2 driving cycles).
- DTCs P0137 and P0157 indicate an open or short circuit in the HO2 sensor
(2 driving cycles). The ECM stores the DTCs when the impedance of the
sensor exceeds the threshold 15 kΩ.
5. Extremely High Output Voltage of Heated Oxygen (HO2) Sensor (DTC P0138 or P0158)
The ECM continuously monitors the HO2 sensor output voltage while the engine is running.
DTC P0138 or P0158 is stored if the HO2 sensor voltage output is more than 1.2 V for 10 seconds or more.
6. Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage During Fuel Cut (P0139 or P0159)
The
sensor output voltage drops to below 0.2 V (extremely lean status)
immediately when the vehicle decelerates and fuel cut is operating. If
the voltage does not drop to below 0.2 V when accumulated intake air
mass is more than 15.3 g, the system determines that the sensor response
has deteriorated, illuminates the MIL and stores a DTC. 7. Abnormal Voltage Output of Heated Oxygen Sensor during Fuel Cut from Rich Condition (P013A and P013C)
If
the sensor output voltage does not drop from 0.35 to 0.2 V immediately
when the vehicle decelerates and fuel cut is operating, the ECM
illuminates the MIL and stores a DTC. MONITOR STRATEGY |
Related DTCs | P0136: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 1) output voltage (Abnormal voltage output)
P0136: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 1) impedance (Low) P0137: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 1) output voltage (Low voltage)
P0137: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 1) impedance (High) P0138: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 1) output voltage (Extremely high)
P0139: Heated oxygen sensor output voltage during fuel cut (for Bank 1)
P013A: Heated oxygen sensor response rate during fuel cut from rich condition
P013C: Heated oxygen sensor response rate during fuel cut from rich condition
P0156: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 2) output voltage (Abnormal voltage output)
P0156: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 2) impedance (Low) P0157: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 2) output voltage (Low voltage)
P0157: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 2) impedance (High) P0158: Heated oxygen sensor (for Bank 2) output voltage (Extremely high)
P0159: Heated oxygen sensor output voltage during fuel cut (for Bank 2) | |
Required Sensors/Components (Main) | Heated oxygen sensor | |
Required Sensors/Components (Related) | Crankshaft
position sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor, mass air flow
meter, throttle position sensor and air fuel ratio sensor | |
Frequency of Operation | Once per driving cycle: Active air-fuel ratio control detection, heated oxygen sensor abnormal voltage during fuel cut
Continuous: Other | | Duration |
20 seconds: Active air-fuel ratio control detection 90 seconds: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (High)
30 seconds: Heated oxygen sensor impedance (Low) 10 seconds: Output voltage (Extremely high)
7 seconds: Heated oxygen sensor voltage (During fuel cut) 7 seconds: Heated oxygen sensor response rate during fuel cut from rich condition | |
MIL Operation | 2 driving cycles: P0136, P0137, P0138, P0139, P0156, P0157, P0158 and P0159
1 driving cycles: P013A and P013C | |
Sequence of Operation | None | TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS All |
Monitor runs whenever following DTCs not present |
P0016, P0018 (VVT system - Misalignment) P0017, P0019 (Exhaust VVT system - Misalignment)
P0031, P0032, P0051, P0052, P101D, P103D (Air fuel ratio sensor heater)
P0037, P0038, P0057, P0058, P102D, P105D (Rear oxygen sensor heater)
P006A, P0107, P0108 (Manifold absolute pressure) P0102, P0103 (Mass air flow meter)
P0112, P0113 (Intake air temperature sensor) P0115, P0117, P0118 (Engine coolant temperature sensor)
P0120, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0220, P0222, P0223, P2135 (Throttle position sensor)
P0125 (Insufficient coolant temperature for closed loop fuel control)
P0128 (Thermostat) P014C,
P014D, P014E, P014F, P015A, P015B, P015C, P015D, P2195, P2196, P2197,
P2198, P2237, P2238, P2239, P2240, P2241, P2242, P2252, P2253, P2255,
P2256 (Air fuel ratio sensor) P0171, P0172, P0174, P0175 (Fuel system)
P0301 - P0308 (Misfire) P0327, P0328, P0332, P0333 (Knock Sensor)
P0335 (Crankshaft position sensor) P1340 (Camshaft position sensor)
P0401 (EGR system) P0412, P0415, P0418, P0419, P1613, P1614 (Secondary Air Injection System Control)
P0451, P0452, P0453 (Evaporative Emission System Pressure Sensor) P0500 (Vehicle speed sensor)
P219A, P219B, P219C, P219D, P219E, P219F, P21A0, P21A1, P21A2, P21A3 (Air-fuel ratio imbalance)
P2440, P2441, P2442, P2443, P2444, P2445, P2446, P2447 (Secondary Air Injection System) | Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (Abnormal Voltage Output and Low Voltage) |
Active air-fuel ratio control | Executing | |
Active air-fuel ratio control begins when all of following conditions met: |
- | | Battery voltage |
11 V or more | | Engine coolant temperature |
75°C (167°F) or more | | Atmospheric pressure |
76 kPa(abs) [570 mmHg(abs)] or higher | |
Idling | OFF | |
Engine RPM | Less than 3200 rpm | |
A/F sensor status | Activated | |
Fuel system status | Closed loop | |
Fuel cut | OFF | |
Engine load | 10 to 75% | |
Transmission gear | 4th or higher | Heated Oxygen Sensor Impedance (Low) |
Battery voltage | 11 V or more | |
Estimated rear HO2 sensor temperature |
Less than 700°C (1292°F) | |
ECM monitor | Completed | |
DTC P0607 | Not set | Heated Oxygen Sensor Impedance (High) |
Battery voltage | 11 V or more | |
Estimated rear HO2 sensor temperature |
450 to 750°C (842 to 1382°F) | |
ECM monitor | Completed | |
DTC P0607 | Not set | Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (Extremely High) |
Battery voltage | 11 V or more | |
Time after engine start | 2 seconds or more | Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage During Fuel Cut |
Engine coolant temperature | 75°C (167°F) or higher | |
Estimated catalyst temperature | 400°C (752°F) or higher | |
Fuel cut | ON | Heated Oxygen Sensor Response Rate during Fuel Cut from Rich Condition |
Battery voltage | 11 V or higher | |
Engine coolant temperature | 75°C (167°F) or higher | |
Estimated catalyst temperature | 400°C (752°F) or higher | |
Fuel cut | ON | TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (Abnormal Voltage Output) |
All of following conditions (a), (b) and (c) met |
- | | (a) Commanded air-fuel ratio |
14.3 or less | | (b) Rear HO2 sensor voltage |
0.21 to 0.66 V | | (c) OSC (Oxygen Storage Capacity of Catalyst) |
2 g or more | Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (Low Voltage) |
All of following conditions (a), (b) and (c) met |
- | | (a) Commanded air-fuel ratio |
14.3 or less | | (b) Rear HO2 sensor voltage |
Less than 0.21 V | | (c) OSC |
2 g or more | Heated Oxygen Sensor Impedance (Low) |
Duration following condition met | 30 seconds or more | |
Heated oxygen sensor impedance | Less than 5 Ω | Heated Oxygen Sensor Impedance (High) |
Duration following condition met | 90 seconds or more | |
Heated oxygen sensor impedance | 15 kΩ or more | Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage (Extremely High) |
Duration following condition met | 10 seconds or more | |
Heated oxygen sensor voltage | 1.2 V or more | Heated Oxygen Sensor Output Voltage During Fuel Cut |
Total airflow volume reached after start of fuel-cut while heated oxygen sensor voltage remains at 0.2 V or higher |
More than 15.3 g | Heated Oxygen Sensor Response Rate during Fuel Cut from Rich Condition |
Duration that heated oxygen sensor voltage drops from 0.35 to 0.2 V during fuel cut (Normalized) |
1 second or more | COMPONENT OPERATING RANGE |
Duration following condition met | 30 seconds or more | |
Heated oxygen sensor voltage | Varies between 0.1 and 0.9 V | MONITOR RESULT
Refer to Checking Monitor Status (See page  ). ). CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN
HINT:
- This confirmation driving pattern is used in the "Perform Confirmation
Driving Pattern" procedure of the following diagnostic troubleshooting
procedure.
- Performing this confirmation driving pattern will activate the Heated
Oxygen (HO2) sensor monitor (The catalyst monitor is performed
simultaneously). This is very useful for verifying the completion of a
repair.
P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 and P0158
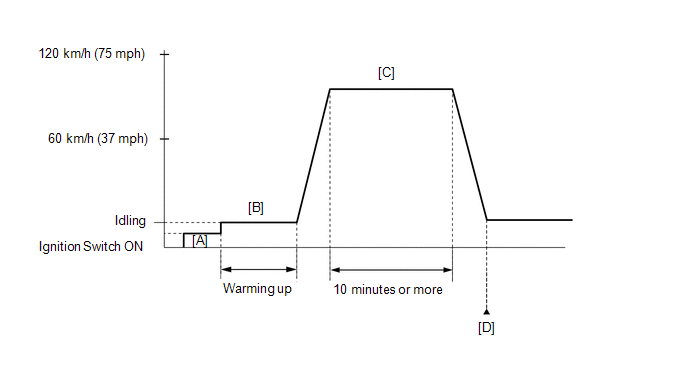
- Connect the Techstream to the DLC3.
- Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the Techstream on.
- Clear the DTCs (even if no DTCs are stored, perform the clear DTC operation).
- Turn the ignition switch off and wait for at least 30 seconds.
- Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the Techstream on [A].
- Start the engine and warm it up until the ECT reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher [B].
- With the transmission in 4th gear or higher, drive the vehicle at 60 to 120 km/h (37 to 75 mph) for 10 minutes or more [C].
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Trouble Codes [D].
- Read the pending DTCs.
HINT:
- If a pending DTC is output, the system is malfunctioning.
- If a pending DTC is not output, perform the following procedure.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
- Input the DTC: P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 or P0158.
- Check the DTC judgment result.
|
Techstream Display |
Description |
|
NORMAL |
- DTC judgment completed
- System normal
|
|
ABNORMAL |
- DTC judgment completed
- System abnormal
|
|
INCOMPLETE |
- DTC judgment not completed
- Perform driving pattern after confirming DTC enabling conditions
|
|
N/A |
- Unable to perform DTC judgment
- Number of DTCs which do not fulfill DTC preconditions has reached ECU memory limit
|
HINT:
- If the judgment result shows NORMAL, the system is normal.
- If the judgment result shows ABNORMAL, the system has a malfunction.
- If the judgment result shows INCOMPLETE or N/A, perform steps [C] through [D].
- If no pending DTC is output, perform a universal trip and check for permanent DTCs (See page
 ). ).
HINT:
- If a permanent DTC is output, the system is malfunctioning.
- If no permanent DTC is output, the system is normal.
P0139, P013A, P013C and P0159
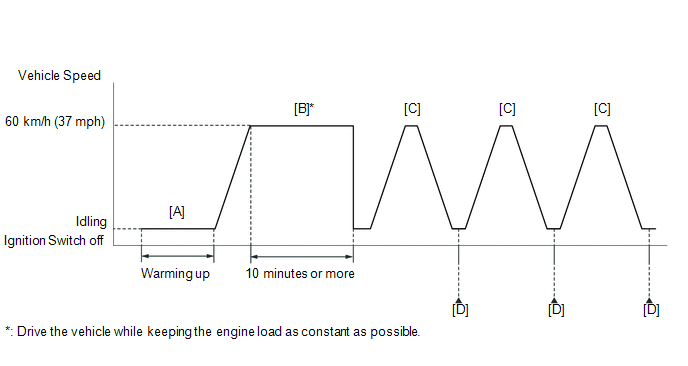
- Connect the Techstream to the DLC3.
- Turn the ignition switch to ON.
- Turn the Techstream on.
- Clear DTCs (even if no DTCs are stored, perform the clear DTC operation).
- Turn the ignition switch off and wait for at least 30 seconds.
- Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the Techstream on.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Monitor / Current Monitor.
- Check that Catalyst Efficiency / Current is Incomplete.
- Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature is 75°C (167°F) or higher [A].
- Drive the vehicle at approximately 60 km/h (37 mph) for 10 minutes or more [B].
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
HINT:
Drive the vehicle while keeping the engine load as constant as possible.
- Drive the vehicle at 60 km/h (37 mph), and then decelerate the vehicle
by releasing the accelerator pedal for 5 seconds or more to perform the
fuel-cut [C].
CAUTION:
When performing the confirmation driving pattern, obey all speed limits and traffic laws.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Monitor / Current Monitor / O2 Sensor / RL F/C B1S2, RL F/C B2S2 [D].
- Check the Test Value for RL F/C B1S2, RL F/C B2S2.
HINT:
If Test Value displays 0, perform step [C] until it displays a value larger than 0, as the O2 sensor monitor is not finished.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Trouble Codes.
- Read the pending DTC [D].
HINT:
- If a pending DTC is output, the system is malfunctioning.
- If a pending DTC is not output, perform the following procedure.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
- Input the DTC: P0139, P013A, P013C or P0159.
- Check the DTC judgment result.
|
Techstream Display |
Description |
|
NORMAL |
- DTC judgment completed
- System normal
|
|
ABNORMAL |
- DTC judgment completed
- System abnormal
|
|
INCOMPLETE |
- DTC judgment not completed
- Perform driving pattern after confirming DTC enabling conditions
|
|
N/A |
- Unable to perform DTC judgment
- Number of DTCs which do not fulfill DTC preconditions has reached ECU memory limit
|
HINT:
- If the judgment result shows ABNORMAL, the system has a malfunction.
- If the judgment result shows NORMAL, the system is normal.
- If the judgment result shows INCOMPLETE or N/A, drive the vehicle with the shift lever in S, and then perform step [C] again.
- If no pending DTC is output, perform a universal trip and check for permanent DTCs (See page
 ). ).
HINT:
- If a permanent DTC is output, the system is malfunctioning.
- If no permanent DTC is output, the system is normal.
WIRING DIAGRAM
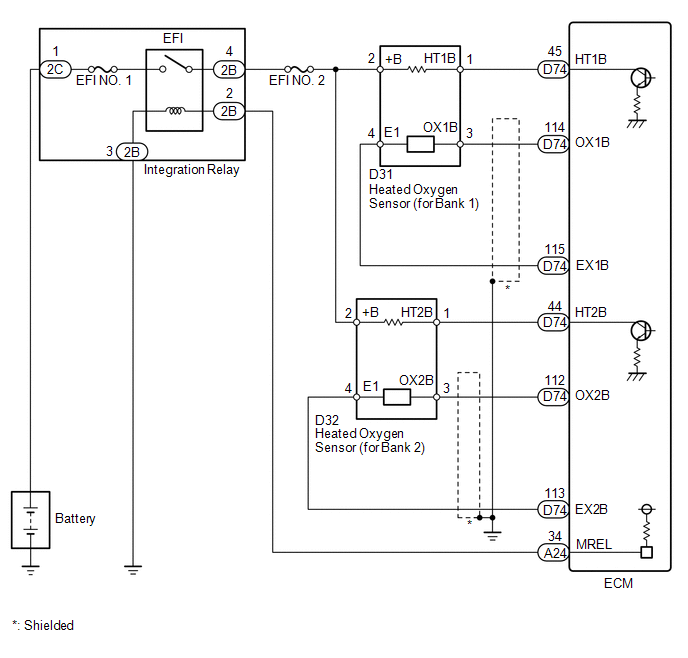 CAUTION / NOTICE / HINT
HINT: Malfunctioning
areas can be identified by performing the Control the Injection Volume
for A/F Sensor function provided in the Active Test. The Control the
Injection Volume for A/F Sensor function can help to determine whether
the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor, Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor and other
potential trouble areas are malfunctioning. The
following instructions describe how to conduct the Control the Injection
Volume for A/F Sensor operation using the Techstream.
- Connect the Techstream to the DLC3.
- Start the engine and turn the Techstream on.
- Warm up the engine at an engine speed of 2500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
- Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor.
- Perform the Active Test operation with the engine in an idling condition
(press the RIGHT or LEFT button to change the fuel injection volume).
- Monitor the output voltages of the A/F and HO2 sensors (AFS Voltage B1S1
and O2S B1S2 or AFS Voltage B2S1 and O2S B2S2) displayed on the
Techstream.
HINT:
- Change the fuel injection volume within the range of -12.5% to +12.5%.
- The air fuel ratio sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the
heated oxygen sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20
seconds.
- If the sensor output voltage does not change (almost no reaction) while
performing the Active Test, the sensor may be malfunctioning.
|
Techstream Display (Sensor) |
Injection Volume | Status |
Voltage | | AFS Voltage B1S1 or AFS Voltage B2S1
(A/F) | +12.5% |
Rich | Below 3.1 V | |
AFS Voltage B1S1 or AFS Voltage B2S1 (A/F) |
-12.5% | Lean |
Higher than 3.4 V | |
O2S B1S2 or O2S B2S2 (HO2) |
+12.5% | Rich |
Higher than 0.55 V | |
O2S B1S2 or O2S B2S2 (HO2) |
-12.5% | Lean |
Below 0.4 V | NOTICE: The
Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and
the Heated Oxygen (HO2) sensor has a maximum output delay of
approximately 20 seconds. 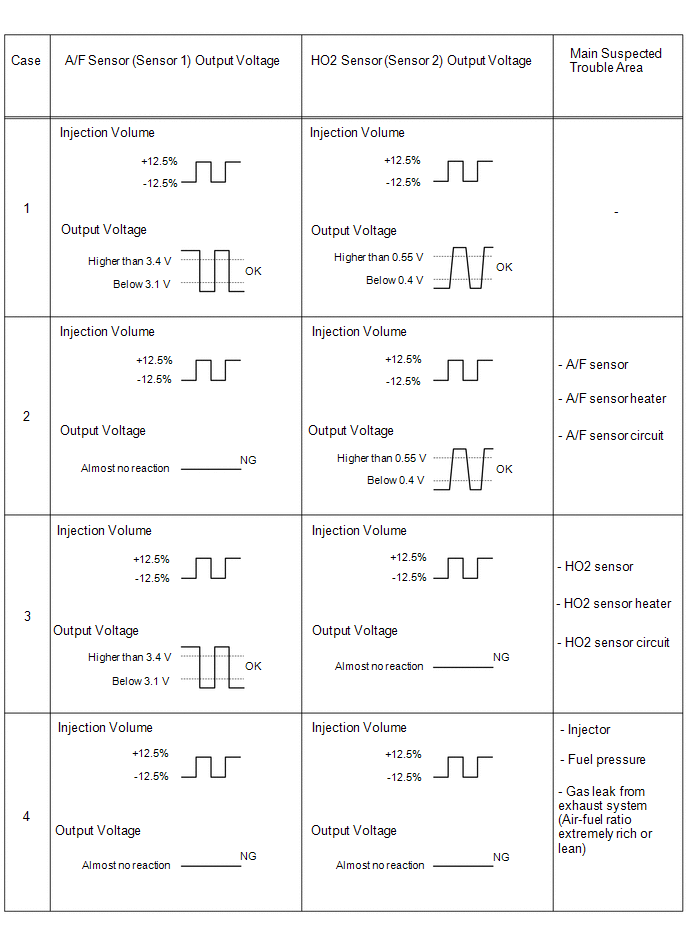
HINT:
PROCEDURE
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Turn the ignition switch to ON.
(c) Turn the Techstream on. (d) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Trouble Codes.
(e) Read DTCs. Result |
Result | Proceed to | |
P0138 or P0158 is output |
A | | P0137 or P0157 is output |
B | | P0136 or P0156 is output |
C | | P0139, P013A, P013C or P0159 is output |
D | | P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 or P0158 and other DTCs are output |
E |
| B |
 | GO TO STEP 8 |
| C |
 | GO TO STEP 4 |
| D |
 | GO TO STEP 21 |
| E |
 | GO TO DTC CHART |
|
A |
 | |
| 2. |
INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (CHECK FOR SHORT) |
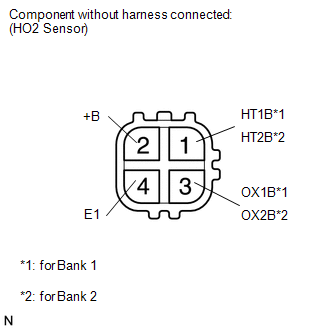 (a) Disconnect the HO2 sensor connector.
(b) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard Resistance: |
Tester Connection | Condition |
Specified Condition | |
2 (+B) - 3 (OX1B) | Always |
10 kΩ or higher | |
2 (+B) - 3 (OX2B) | Always |
10 kΩ or higher | |
2 (+B) - 4 (E1) | Always |
10 kΩ or higher | HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the heated oxygen sensor (See page
 ). ).
| NG |  |
REPLACE HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR |
|
OK |
 | |
| 3. |
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CHECK FOR SHORT) |
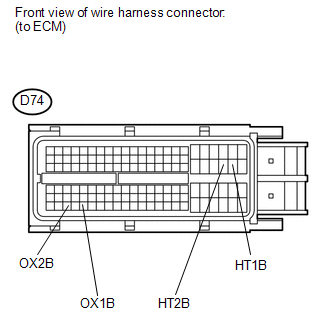 (a) Turn the ignition switch off and wait for 5 minutes.
(b) Disconnect the ECM connector. (c) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard Resistance: |
Tester Connection | Condition |
Specified Condition | |
D74-45 (HT1B) - D74-114 (OX1B) |
Always | 10 kΩ or higher | |
D74-44 (HT2B) - D74-112 (OX2B) |
Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| OK |
 | REPLACE ECM |
| NG |
 | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
| 4. |
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING TECHSTREAM (CONTROL THE INJECTION VOLUME FOR A/F SENSOR) |
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Start the engine. (c) Turn the Techstream on.
(d) Warm up the engine. (e)
Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test /
Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor / Data List / O2S B1S2 or
O2S B2S2. (f) Change the fuel injection volume
using the Techstream, monitoring the voltage output of the HO2 sensors
displayed on the Techstream.
HINT:
- Change the fuel injection volume within the range of -12.5% to +12.5%.
- The air fuel ratio sensor has an output delay of a few seconds and the
heated oxygen sensor has a maximum output delay of approximately 20
seconds.
Standard voltage: Fluctuates between 0.4 V or less and 0.55 V or more.
| NG |
 | GO TO STEP 8 |
|
OK |
 | |
| 5. |
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING TECHSTREAM (INJECTION VOLUME FOR A/F SENSOR) |
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Turn the Techstream on.
(c) Start the engine. (d) Warm up the engine. (e) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the Injection Volume for A/F Sensor.
(f)
Change the fuel injection volume using the Techstream, and monitor the
voltage output of the Air-Fuel Ratio (A/F) and HO2 sensors displayed on
the Techstream.
HINT:
| NG |
 | GO TO STEP 16 |
|
OK |
 | |
| 6. |
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING TECHSTREAM (CONTROL THE EGR STEP POSITION) |
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
HINT:
- When performing the Active Test, make sure the shift lever is in P or N.
- The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off.
(c) Turn the Techstream on. (d) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the EGR Step Position.
(e)
Confirm the Throttle Idle Position is ON and check the engine idling
condition and MAP values in the Data List while performing the Active
Test.
HINT:
- Do not leave the EGR valve open for 10 seconds or more during the Active Test.
- Be sure to return the EGR valve to step 0 when the Active Test is completed.
OK: MAP and idling condition change in response to EGR step position as follows.
Standard: |
- | EGR Step Position (Active Test) | |
0 Steps | 0 to 30 Steps | |
Idling condition | Steady idling |
Idling changes from steady to rough idling or engine stall | |
MAP (Data List) |
20 to 40 kPa (150 to 300 mmHg) |
MAP value is at least +10 kPa (75 mmHg) higher than when EGR valve is fully closed |
| OK |
 | CHECK
EXTREMELY RICH OR LEAN ACTUAL AIR FUEL RATIO AND REPAIR CAUSE (FUEL
INJECTOR ASSEMBLY, FUEL PRESSURE, GAS LEAK FROM SYSTEM) |
|
NG |
 | |
| 7. |
INSPECT EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY | (a) Remove the EGR valve assembly (See page
 ). ). (b) Check if the EGR valve is stuck open.
OK: EGR valve is tightly closed. HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repairs" after replacing the EGR valve assembly (See page
 ). ).
| OK |  |
CHECK
EXTREMELY RICH OR LEAN ACTUAL AIR FUEL RATIO AND REPAIR CAUSE (FUEL
INJECTOR ASSEMBLY, FUEL PRESSURE, GAS LEAK FROM SYSTEM) |
| NG |
 | REPLACE EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY |
| 8. |
CHECK FOR EXHAUST GAS LEAK | (a) Check for exhaust gas leak.
OK: No gas leak. HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after repairing or replacing the exhaust system (See page
 ). ).
| NG |  |
REPAIR OR REPLACE EXHAUST GAS LEAK POINT |
|
OK |
 | |
| 9. |
INSPECT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HEATER RESISTANCE) |

| NG |  |
REPLACE HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR |
|
OK |
 | |
| 10. |
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR - ECM) |
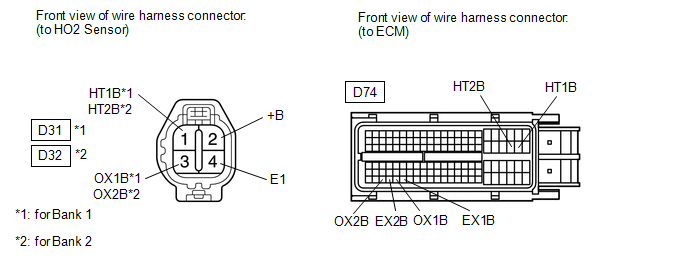 (a) Disconnect the HO2 sensor connector.
(b) Disconnect the ECM connector. (c) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard Resistance: |
Tester Connection | Condition |
Specified Condition | |
D31-1 (HT1B) - D74-45 (HT1B) |
Always | Below 1 Ω | |
D31-3 (OX1B) - D74-114 (OX1B) |
Always | Below 1 Ω | |
D31-4 (E1) - D74-115 (EX1B) |
Always | Below 1 Ω | |
D32-1 (HT2B) - D74-44 (HT2B) |
Always | Below 1 Ω | |
D32-3 (OX2B) - D74-112 (OX2B) |
Always | Below 1 Ω | |
D32-4 (E1) - D74-113 (EX2B) |
Always | Below 1 Ω | |
D31-1 (HT1B) or D74-45 (HT1B) - Body ground |
Always | 10 kΩ or higher | |
D31-3 (OX1B) or D74-114 (OX1B) - Body ground |
Always | 10 kΩ or higher | |
D32-1 (HT2B) or D74-44 (HT2B) - Body ground |
Always | 10 kΩ or higher | |
D32-3 (OX2B) or D74-112 (OX2B) - Body ground |
Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| NG |
 | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
OK |
 | |
| 11. |
REPLACE HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR | (a) Replace the heated oxygen sensor (See page
 ). ). HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the heated oxygen sensor (See page
 ). ).
|
NEXT |
 | |
| 12. |
PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN | (a) Perform the Confirmation Driving Pattern (P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 and P0158).
|
NEXT |
 | |
| 13. |
CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 OR P0158 IS OUTPUT AGAIN) |
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Turn the Techstream on.
(c) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
(d) Input DTCs: P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 and P0158. (e)
Check that the DTC monitor is NORMAL. If the DTC monitor is INCOMPLETE,
perform the drive pattern increasing the vehicle speed. Result |
Result | Proceed to | |
ABNORMAL (DTC P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 or P0158 is output) |
A | | NORMAL (DTC is not output) |
B |
| B |
 | END |
|
A |
 | |
| 14. |
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING TECHSTREAM (CONTROL THE EGR STEP POSITION) |
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
HINT:
- When performing the Active Test, make sure the shift lever is in P or N.
- The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off.
(c) Turn the Techstream on. (d) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the EGR Step Position.
(e)
Confirm the Throttle Idle Position is ON and check the engine idling
condition and MAP values in the Data List while performing the Active
Test.
HINT:
- Do not leave the EGR valve open for 10 seconds or more during the Active Test.
- Be sure to return the EGR valve to step 0 when the Active Test is completed.
OK: MAP and idling condition change in response to EGR step position as follows.
Standard: |
- | EGR Step Position (Active Test) | |
0 Steps | 0 to 30 Steps | |
Idling condition | Steady idling |
Idling changes from steady to rough idling or engine stall | |
MAP (Data List) |
20 to 40 kPa (150 to 300 mmHg) |
MAP value is at least +10 kPa (75 mmHg) higher than when EGR valve is fully closed |
HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the air fuel ratio sensor (See page
 ). ).
| OK |  |
REPLACE AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR |
|
NG |
 | |
| 15. |
INSPECT EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY | (a) Remove the EGR valve assembly (See page
 ). ). (b) Check if the EGR valve is stuck open.
OK: EGR valve is tightly closed. HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the EGR valve assembly or air fuel ratio sensor (See page
 ). ).
| OK |  |
REPLACE AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR |
| NG |
 | REPLACE EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY |
| 16. |
REPLACE AIR FUEL RATIO SENSOR | (a) Replace the air fuel ratio sensor (See page
 ). ). HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the air fuel ratio sensor (See page
 ). ).
|
NEXT |
 | |
| 17. |
PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN | (a) Perform the Confirmation Driving Pattern (P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 and P0158).
|
NEXT |
 | |
| 18. |
CHECK WHETHER DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 OR P0158 IS OUTPUT AGAIN) |
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Turn the Techstream on.
(c) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
(d) Input DTCs: P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 and P0158. (e)
Check that the DTC monitor is NORMAL. If the DTC monitor is INCOMPLETE,
perform the drive pattern increasing the vehicle speed. Result |
Result | Proceed to | |
ABNORMAL (DTC P0136, P0137, P0138, P0156, P0157 or P0158 is output) |
A | | NORMAL (DTC is not output) |
B |
| B |
 | END |
|
A |
 | |
| 19. |
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING TECHSTREAM (CONTROL THE EGR STEP POSITION) |
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
HINT:
- When performing the Active Test, make sure the shift lever is in P or N.
- The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off.
(c) Turn the Techstream on. (d) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the EGR Step Position.
(e)
Confirm the Throttle Idle Position is ON and check the engine idling
condition and MAP values in the Data List while performing the Active
Test.
HINT:
- Do not leave the EGR valve open for 10 seconds or more during the Active Test.
- Be sure to return the EGR valve to step 0 when the Active Test is completed.
OK: MAP and idling condition change in response to EGR step position as follows.
Standard: |
- | EGR Step Position (Active Test) | |
0 Steps | 0 to 30 Steps | |
Idling condition | Steady idling |
Idling changes from steady to rough idling or engine stall | |
MAP (Data List) |
20 to 40 kPa (150 to 300 mmHg) |
MAP value is at least +10 kPa (75 mmHg) higher than when EGR valve is fully closed |
HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the heated oxygen sensor (See page
 ). ).
| OK |  |
REPLACE HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR |
|
NG |
 | |
| 20. |
INSPECT EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY | (a) Remove the EGR valve assembly (See page
 ). ). (b) Check if the EGR valve is stuck open.
OK: EGR valve is tightly closed. HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the EGR valve assembly or heated oxygen sensor (See page
 ). ).
| OK |  |
REPLACE HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR |
| NG |
 | REPLACE EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY |
| 21. |
CHECK FOR EXHAUST GAS LEAK | (a) Check for exhaust gas leak.
OK: No gas leak. HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after repairing or replacing the exhaust system (See page
 ). ).
| NG |  |
REPAIR OR REPLACE EXHAUST GAS LEAK POINT |
|
OK |
 | |
| 22. |
CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (CHECK FOR SHORT) |
 (a) Turn the ignition switch off and wait for 5 minutes.
(b) Disconnect the ECM connector. (c) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the table below.
Standard Resistance: |
Tester Connection | Condition |
Specified Condition | |
D74-45 (HT1B) - D74-114 (OX1B) |
Always | 10 kΩ or higher | |
D74-44 (HT2B) - D74-112 (OX2B) |
Always | 10 kΩ or higher |
| NG |
 | REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR |
|
OK |
 | |
| 23. |
PERFORM CONFIRMATION DRIVING PATTERN | (a) Perform the Confirmation Driving Pattern (P0139, P013A, P013C and P0159).
|
NEXT |
 | |
| 24. |
READ DTC OUTPUT (DTC P0139, P013A, P013C OR P0159 IS OUTPUTAGAIN) |
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Turn the Techstream on.
(c) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Utility / All Readiness.
(d) Input DTCs: P0139, P013A, P013C or P0159. (e)
Check that the DTC monitor is NORMAL. If the DTC monitor is INCOMPLETE,
perform the drive pattern increasing the vehicle speed. Result |
Result | Proceed to | |
ABNORMAL (DTC P0139, P013A, P013C or P0159 is output) |
A | | NORMAL (DTC is not output) |
B |
| B |
 | CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS |
|
A |
 | |
| 25. |
PERFORM ACTIVE TEST USING TECHSTREAM (CONTROL THE EGR STEP POSITION) |
(a) Connect the Techstream to the DLC3. (b) Start the engine and warm it up until the engine coolant temperature reaches 75°C (167°F) or higher.
HINT:
- When performing the Active Test, make sure the shift lever is in P or N.
- The A/C switch and all accessory switches should be off.
(c) Turn the Techstream on. (d) Enter the following menus: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / Control the EGR Step Position.
(e)
Confirm the Throttle Idle Position is ON and check the engine idling
condition and MAP values in the Data List while performing the Active
Test.
HINT:
- Do not leave the EGR valve open for 10 seconds or more during the Active Test.
- Be sure to return the EGR valve to step 0 when the Active Test is completed.
OK: MAP and idling condition change in response to EGR step position as follows.
Standard: |
- | EGR Step Position (Active Test) | |
0 Steps | 0 to 30 Steps | |
Idling condition | Steady idling |
Idling changes from steady to rough idling or engine stall | |
MAP (Data List) |
20 to 40 kPa (150 to 300 mmHg) |
MAP value is at least +10 kPa (75 mmHg) higher than when EGR valve is fully closed |
HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the heated oxygen sensor (See page
 ). ).
| OK |  |
REPLACE HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR |
|
NG |
 | |
| 26. |
INSPECT EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY | (a) Remove the EGR valve assembly (See page
 ). ). (b) Check if the EGR valve is stuck open.
OK: EGR valve is tightly closed. HINT: Perform "Inspection After Repair" after replacing the EGR valve assembly or heated oxygen sensor (See page
 ). ).
| OK |  |
REPLACE HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR |
| NG |
 | REPLACE EGR VALVE ASSEMBLY | |











